Chronic kidney disease
Kidney failure - chronic; Renal failure - chronic; Chronic renal insufficiency; Chronic kidney failure; Chronic renal failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body.
Causes
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) slowly gets worse over months or years. You may not notice any symptoms for some time. The loss of function may be so slow that you do not have symptoms until your kidneys have almost stopped working.
The final stage of CKD is called end-stage renal disease (ESRD). At this stage, the kidneys are no longer able to remove enough wastes and excess fluids from the body. At this point, you would need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Diabetes and high blood pressure are the 2 most common causes and account for most cases.
Many other diseases and conditions can damage the kidneys, including:
- Autoimmune disorders (such as systemic lupus erythematosus and scleroderma)
- Birth defects of the kidneys (such as polycystic kidney disease)
- Some toxic chemicals
- Injury to the kidney
- Kidney stones and infection
- Problems with the arteries feeding the kidneys
- Some medicines, such as pain and cancer medicines
- Backward flow of urine into the kidneys (reflux nephropathy)
CKD leads to a buildup of fluid and waste products in the body. This condition affects most body systems and functions, including:
- High blood pressure
- Low blood cell count
- Vitamin D and bone health
Symptoms
The early symptoms of CKD are the same as for many other illnesses. These symptoms may be the only sign of a problem in the early stages.
Symptoms may include:
- Appetite loss
- General ill feeling and fatigue
- Headaches
- Itching (pruritus) and dry skin
- Nausea
- Weight loss without trying to lose weight
Symptoms that may occur when kidney function has gotten worse include:
- Abnormally dark or light skin
- Bone pain
- Drowsiness or problems concentrating or thinking
- Numbness or swelling in the hands and feet
- Muscle twitching or cramps
- Breath odor
- Easy bruising, or blood in the stool
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent hiccups
- Problems with sexual function
- Menstrual periods stop (amenorrhea)
- Shortness of breath
- Sleep problems
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
Most people will have high blood pressure at all stages of CKD. During an exam, your health care provider may also hear abnormal heart or lung sounds in your chest. You may have signs of nerve damage during a nervous system exam.
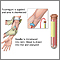
A urinalysis may show protein or other changes in your urine. These changes may appear 6 to 10 months or more before symptoms appear.
Tests that check how well the kidneys are working include:
- Creatinine clearance
- Creatinine levels
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
CKD changes the results of several other tests. You will need to have the following tests as often as every 2 to 3 months when kidney disease gets worse:
Other tests that may be done to look for the cause or type of kidney disease include:
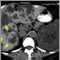
- CT scan of the abdomen
- MRI of the abdomen
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
- Kidney biopsy
- Kidney scan
- Kidney ultrasound
This disease may also change the results of the following tests:
- Erythropoietin
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Bone density test
- Vitamin D level
Treatment
Blood pressure control will slow further kidney damage.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are used most often.
- The goal is to keep blood pressure at or below 130/80 mm Hg.
Making lifestyle changes can help protect the kidneys, and prevent heart disease and stroke, such as:
- DO NOT smoke.
- Eat meals that are low in fat and cholesterol.
- Get regular exercise (talk to your provider or nurse before starting to exercise).
- Take medicines to lower your cholesterol, if needed.
- Keep your blood sugar under control.
- Avoid eating too much salt or potassium.
Always talk to your kidney specialist before taking any over-the-counter medicine. This includes vitamins, herbs and supplements. Make sure all of the providers you visit know you have CKD. Other treatments may include:
- Medicines called phosphate binders, to help prevent high phosphorous levels
- Extra iron in the diet, iron pills, iron given through a vein (intravenous iron) special shots of a medicine called erythropoietin, and blood transfusions to treat anemia
- Extra calcium and vitamin D (always talk to your provider before taking)
Your provider may have you follow a special diet for CKD.
- Limiting fluids
- Eating less protein
- Restricting phosphorous and other electrolytes
- Getting enough calories to prevent weight loss
All people with CKD should be up-to-date on the following vaccinations:
Support Groups
More information and support for people with CKD and their families can be found at a kidney disease support group.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Many people are not diagnosed with CKD until they have lost most of their kidney function.
There is no cure for CKD. If it worsens to ESRD, and how quickly, depends on:
- The cause of kidney damage
- How well you take care of yourself
Kidney failure is the last stage of CKD. This is when your kidneys can no longer support our body's needs.
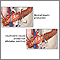
Your provider will discuss dialysis with you before you need it. Dialysis removes waste from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do their job.
In most cases, you will go to dialysis when you have only 10 to 15% of your kidney function left.
Even people who are waiting for a kidney transplant may need dialysis while waiting.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Anemia
- Bleeding from the stomach or intestines
- Bone, joint, and muscle pain
- Changes in blood sugar
- Damage to nerves of the legs and arms (peripheral neuropathy)
- Dementia
- Fluid buildup around the lungs (pleural effusion)
- Heart and blood vessel complications
- High phosphorous levels
- High potassium levels
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Increased risk of infections
- Liver damage or failure
- Malnutrition
- Miscarriages and infertility
- Seizures
- Swelling (edema)
- Weakening of the bones and increased risk of fractures
Prevention
Treating the condition that is causing the problem may help prevent or delay CKD. People who have diabetes should control their blood sugar and blood pressure levels and should not smoke.
References
Christov M, Sprague SM. Chronic kidney disease - mineral bone disorder. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 53.
Grams ME, McDonald SP. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease and dialysis. In: Feehally J, Floege J, Tonelli M, Johnson RJ, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 77.
Taal MW. Classification and management of chronic kidney disease. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 59.
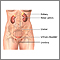
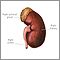
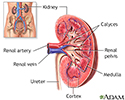
Kidney anatomy - illustration
Kidney anatomy
illustration
Kidney - blood and urine flow - illustration
Kidney - blood and urine flow
illustration
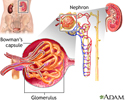
Glomerulus and nephron - illustration
Glomerulus and nephron
illustration
Review Date: 7/27/2021
Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.