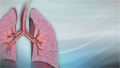
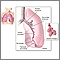
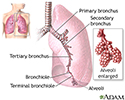
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder.
Some coughs are dry. Others are productive. A productive cough is one that brings up mucus. Mucus is also called phlegm or sputum.
Coughs can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute coughs usually begin rapidly and are often due to a cold, flu, or sinus infection. They usually go away after 3 weeks.
- Subacute coughs last 3 to 8 weeks.
- Chronic coughs last longer than 8 weeks.
Common causes of coughing are:
- Allergies that involve the nose or sinuses
- Asthma and COPD (emphysema or chronic bronchitis)
- The common cold and flu
- Lung infections such as pneumonia or acute bronchitis
- Sinusitis with postnasal drip
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Other causes include:
- ACE inhibitors (medicines used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, or kidney diseases)
- Cigarette smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke (or smoking other substances like marijuana)
- Lung cancer
- Lung disease such as bronchiectasis or interstitial lung disease
- Sometimes no specific cause is found
Home Care
If you have asthma or another chronic lung disease, make sure you are taking medicines prescribed by your health care provider.
Here are some tips to help ease your cough:
- If you have a dry, tickling cough, try cough drops or hard candy. Never give these to a child under age 3, because they can cause choking.
- Use a vaporizer or take a steamy shower to increase moisture in the air and help soothe a dry throat.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Liquids help thin the mucus in your throat making it easier to cough it up.
- Do not smoke, and stay away from secondhand smoke.
Medicines you can buy on your own include:
- Guaifenesin helps break up mucus. Follow package instructions on how much to take. Do not take more than the recommended amount. Drink lots of fluids if you take this medicine.
- Decongestants help clear a runny nose and relieve postnasal drip. Check with your provider before taking decongestants if you have high blood pressure.
- Talk to your child's provider before you give children ages 6 years or younger an over-the-counter cough medicine, even if it is labeled for children. These medicines likely do not work for children, and can have serious side effects.
If you have seasonal allergies, such as hay fever:
- Stay indoors during days or times of the day (usually the morning) when airborne allergens are high.
- Keep windows closed and use an air conditioner.
- DO not use fans that draw in air from outdoors.
- Shower and change your clothes after being outside.
If you have allergies year-round, cover your pillows and mattress with dust mite covers, use an air purifier, and avoid pets with fur and other triggers.
Treat the underlying cause (per above) as directed by your health care provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number if you have:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Hives or a swollen face or throat with difficulty swallowing
Call your provider right away if a person with cough has any of the following:
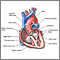
- Heart disease, swelling in your legs, or a cough that gets worse when you lie down (may be signs of heart failure)
- Have come into contact with someone who has tuberculosis
- Unintentional weight loss or night sweats (could be tuberculosis)
- An infant younger than 3 months old who has a cough
- Cough lasts longer than 10 to 14 days
- Cough that produces blood
- Fever (may be a sign of a bacterial infection that requires antibiotics)
- High-pitched sound (called stridor) when breathing in
- Thick, foul-smelling, yellowish-green phlegm (could be a bacterial infection)
- Violent cough that begins rapidly
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a physical exam. You will be asked about your cough. Questions may include:
- When the cough began
- What it sounds like
- If there is pattern to it
- What makes it better or worse
- If you have other symptoms, such as a fever
The provider will examine your ears, nose, throat, and chest.
Tests that may be done include:
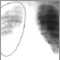
- Chest x-ray or CT scan
- Lung function tests
- Blood tests
- Tests to check the heart, such as an echocardiogram
- Gastroesophageal reflux evaluation tests (for example barium swallow)
Treatment depends on the cause of the cough.
References
Chung KF, Mazzone SB. Cough. In: Broaddus VC, King TE, Ernst JD, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 37.
Kraft M. Approach to the patient with respiratory disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 77.
Review Date: 5/30/2021
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.