Skin lesion aspiration
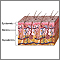
Skin lesion aspiration is the withdrawal of fluid from a skin lesion (sore).
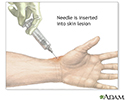
The health care provider inserts a needle into the skin sore or skin abscess, which may contain fluid or pus. Fluid from the sore or abscess is withdrawn. The fluid may be examined under a microscope. A sample of the fluid may also be sent to a lab. There, it is put in a lab dish (called a culture medium) and watched for growth of bacteria, virus or fungi.
If the sore is deep, the provider may inject numbing medicine (anesthetic) into the skin before inserting the needle.
How to Prepare for the Test
You do not need to prepare for this test.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel a pricking sensation as the needle enters the skin.
In many cases, removing the fluid will lessen pressure within the skin sore and ease pain.
Why the Test Is Performed
This test is used to find the cause of a fluid-filled skin lesion. It can be used to diagnose skin infections or cancers.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be a sign of infection caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses. Cancer cells may also be seen.
Risks
There is a small risk of bleeding, mild pain, or infection.
References
Chernecky CC, Berger BJ. Biopsy, site-specific - specimen. In: Chernecky CC, Berger BJ, eds. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:199-202.
Marks JG, Miller JJ. Dermatologic therapy and procedures. In: Marks JG, Miller JJ, eds. Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 4.
Review Date: 11/4/2020
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Senior Associate Consultant, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.