Drug-induced lupus erythematosus
Lupus - drug induced
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder that is triggered by a reaction to a medicine.
Causes
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is similar but not identical to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). It is an autoimmune disorder. This means your body attacks healthy tissue by mistake. It is caused by a reaction to a medicine. Related conditions are drug-induced cutaneous lupus and drug-induced ANCA vasculitis.
The most common medicines known to cause drug-induced lupus erythematosus are:
- Isoniazid
- Hydralazine
- Procainamide
- Tumor-necrosis factor (TNF) alpha inhibitors (such as etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab)
- Minocycline
- Quinidine
Other less common drugs may also cause the condition. These may include:
- Anti-seizure medicines
- Capoten
- Chlorpromazine
- Methyldopa
- Sulfasalazine
- Levamisole, typically as a contaminant of cocaine
Cancer immunotherapy drugs such as pembrolizumab can also cause a variety of autoimmune reactions including drug-induced lupus.
Symptoms of drug-induced lupus tend to occur after taking the drug for at least 3 to 6 months.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
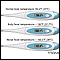
- Fever
- General ill feeling (malaise)
- Joint pain
- Joint swelling
- Loss of appetite
- Pleuritic chest pain
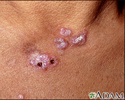
- Skin rash on areas exposed to sunlight
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a physical exam and listen to your chest with a stethoscope. The provider may hear a sound called a heart friction rub or pleural friction rub.
A skin exam shows a rash.
Joints may be swollen and tender.
Tests that may be done include:
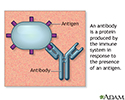
- Antihistone antibody
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) panel
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) panel
- Complete blood count (CBC) with differential
- Comprehensive chemistry panel
- Urinalysis
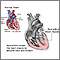
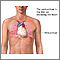
A chest x-ray may show signs of pleuritis or pericarditis (inflammation around the lining of the lung or heart). An ECG may show that the heart is affected.
Treatment
Most of the time, symptoms go away within weeks after stopping the medicine that caused the condition.
Treatment may include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to treat arthritis and pleurisy
- Corticosteroid creams to treat skin rashes
- Antimalarial drugs (hydroxychloroquine) to treat skin and arthritis symptoms
If the condition is affecting your heart, kidney, or nervous system, you may be prescribed high doses of corticosteroids (prednisone, methylprednisolone) and immune system suppressants (azathioprine or cyclophosphamide). This is rare.
When the disease is active, you should wear protective clothing and sunglasses to guard against too much sun.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, drug-induced lupus erythematosus is not as severe as SLE. The symptoms often go away within a few days to weeks after stopping the medicine you were taking. Rarely, kidney inflammation (nephritis) can develop with drug-induced lupus caused by TNF inhibitors or with ANCA vasculitis due to hydralazine or levamisole. Nephritis may require treatment with prednisone and immunosuppressive medicines.
Avoid taking the drug that caused the reaction in future. Symptoms are likely to return if you do so.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Infection
- Thrombocytopenia purpura -- bleeding near the skin surface, resulting from a low number of platelets in the blood
- Hemolytic anemia
- Myocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Nephritis
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
- You develop new symptoms when taking any of the medicines listed above.
- Your symptoms do not get better after you stop taking the medicine that caused the condition.
Prevention
Watch for signs of a reaction if you are taking any of the drugs that can cause this problem.
References
Benfaremo D, Manfredi L, Luchetti MM, Gabrielli A. Musculoskeletal and rheumatic diseases induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review of the literature. Curr Drug Saf. 2018;13(3):150-164. PMID: 29745339 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29745339/.
Radhakrishnan J, Perazella MA. Drug-induced glomerular disease: attention required. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(7):1287-1290. PMID: 25876771 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25876771/.
Richardson BC. Drug-induced lupus. In: Hochberg MC, Gravallese EM, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, eds. Rheumatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 141.
Rubin RL. Drug-induced lupus. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2015;14(3):361-378. PMID: 25554102 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25554102/.
Rubin RL. Drug-induced lupus. In: Tsokos GC, ed. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 2nd ed. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2021:chap 56.
Vaglio A, Grayson PC, Fenaroli P, et al. Drug-induced lupus: traditional and new concepts. Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(9):912-918. PMID: 30005854 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30005854/.
Lupus, discoid - view of lesions on the chest - illustration
Lupus, discoid - view of lesions on the chest
illustration
Antibodies - illustration
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 5/2/2021
Reviewed By: Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.