Charcot foot
Charcot joint; Neuropathic arthropathy; Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy; Charcot arthropathy; Charcot osteoarthropathy; Diabetic Charcot foot
Charcot foot is a condition that affects the bones, joints, and soft tissue in the feet and ankles. It can develop as a result of nerve damage in the feet due to diabetes or other nerve injuries.
Causes
Charcot foot is a rare and disabling disorder. It is a result of nerve damage to the feet. A common cause is peripheral neuropathy.
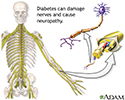
Diabetes is the most common cause of this type of nerve damage. This damage is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. When blood sugar levels are high over a long time, both nerve and blood vessel damage occurs in the arms and legs.
Nerve damage makes it harder to notice the amount of pressure on the foot or if it is being stressed. The result is ongoing small injuries to the bones and ligaments that support the foot.
- You may develop bone stress fractures in your feet, yet never know it.
- Continuing to walk on the fractured bone often leads to further bone and joint damage.
Other factors leading to foot damage include:
- Blood vessel damage from diabetes can increase or change blood flow to the feet. This can lead to bone loss. Weakened bones in the feet increase the risk of fracture.
- Injury to the foot signals the body to produce more inflammation-causing chemicals. This contributes to swelling and bone loss.
Symptoms
Early foot symptoms may include:
- Mild pain and discomfort
- Redness
- Swelling
- Warmth in the affected foot (noticeably warmer than the other foot)
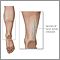
At later stages, bones in the foot break and move out of place, causing the foot or ankle to become deformed.
- A classic sign of Charcot is rocker-bottom foot. This occurs when the bones in middle of the foot collapse. This causes the arch of the foot to collapse and bow downward.
- The toes may curl downward.
Bones that stick out at odd angles can lead to pressure sores and foot ulcers.
- Because the feet are numb, these sores and ulcers may grow wider or deeper before they are noticed.
- High blood sugar also makes it hard for the body to fight infection. As a result, these foot ulcers become infected.
Exams and Tests
Charcot foot is not always easy to diagnose early on. It can be mistaken for sprains, bone infection, arthritis or joint swelling. Your health care provider will take your medical history and examine your foot and ankle.
Blood tests and other lab work may be done to help rule out other causes.
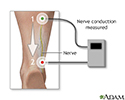
Your provider may check for nerve damage with these tests:
The following tests may be done to check for bone and joint damage:
Foot x-rays may look normal at early stages of the condition. Diagnosis often comes down to recognizing early symptoms of Charcot foot: swelling, redness, and warmth of the affected foot.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to stop bone loss, allow bones to heal, and prevent bones from moving out of place (deformity).
Immobilization. Your provider will have you wear a total contact cast. This will help limit movement of your foot and ankle. You will likely be asked to keep your weight off your foot entirely, so you will need to use crutches, a knee-walker device, or wheelchair.
You will have new casts placed on your foot as the swelling comes down. Healing can take a couple of months or more.
Protective footwear. Once your foot has healed, your provider may suggest footwear to help support your foot and prevent re-injury. These may include:
- Splints
- Braces
- Orthotic insoles
- Charcot restraint orthotic walker, a special boot that provides even pressure to the whole foot
Activity changes. You will always be at risk for Charcot foot coming back or developing in your other foot. So your provider may recommend activity changes, such as limiting your standing or walking, to protect your feet.
Surgery. You may need surgery if you have foot ulcers that keep coming back or severe foot or ankle deformity. Surgery can help stabilize your foot and ankle joints and remove bony areas to prevent foot ulcers.
Ongoing monitoring. You will need to see your provider for checkups and take steps to protect your feet for the rest of your life.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The prognosis depends on the severity of foot deformity and how well you heal without infection. Many people do well with braces, activity changes, and ongoing monitoring.
Possible Complications
Severe deformity of the foot increases the risk of foot ulcers. If ulcers or the underlying bone becomes infected and hard to treat, it may require amputation.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider of you have diabetes and your foot is warm, red, or swollen.
Prevention
Healthy habits can help prevent or delay Charcot foot:
- Keep good control of your blood glucose levels to help prevent or delay Charcot foot. But it can still occur, even in people with good diabetes control.
- Take care of your feet. Check them every day.
- See your foot doctor regularly.
- Check your feet regularly to look for cuts, redness and sores.
- Avoid injuring your feet.
References
American Diabetes Association. 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021.Diabetes Care. 2021;44(Suppl 1):S151-S167. PMID: 33298422. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33298422/.
Baxi O, Yeranosian M, Lin A, Munoz M, Lin S. Orthotic management of neuropathic and dysvascular feet. In: Webster JB, Murphy DP, eds. Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 26.
Brownlee M, Aiello LP, Sun JK, et al. Complications of diabetes mellitus. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37.
Kutschke M, Blankenhorn B. Charcot joint. In: Ferri FF, ed. Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2022. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:356.
Rogers LC, Armstrong DG. Podiatric care. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 116.
Diabetes
Animation
Nerve conduction test - illustration
Nerve conduction test
illustration
Diabetes and nerve damage - illustration
Diabetes and nerve damage
illustration
Diabetic foot care - illustration
Diabetic foot care
illustration
Review Date: 11/12/2020
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.