Esophagitis
Inflammation - esophagus; Erosive esophagitis; Ulcerative esophagitis; Eosinophilic esophagitis
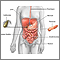
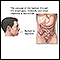
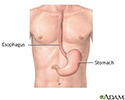
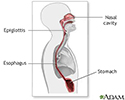
Esophagitis is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus becomes swollen, inflamed, or irritated. The esophagus is the tube that leads from your mouth to the stomach. It is also called the food pipe.
Causes
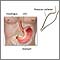
Esophagitis is often caused by stomach fluid that flows back into the food pipe. The fluid contains acid, which irritates the esophageal lining. This problem is called gastroesophageal reflux (GERD). An autoimmune disorder called eosinophilic esophagitis also causes this condition.
The following increase your risk for this condition:
- Alcohol use
- Cigarette smoking
- Surgery or radiation to the chest (for example, treatment for lung cancer)
- Taking certain medicines such as alendronate, doxycycline, ibandronate, risedronate, tetracycline, potassium tablets, and vitamin C, without drinking plenty of water
- Vomiting
- Lying down after eating a large meal
- Obesity
People who have a weakened immune system may develop infections. Infections may lead to swelling of the food pipe. Infection may be due to:
- Fungi or yeast (most often Candida)
- Viruses, such as herpes or cytomegalovirus
Symptoms
The infection or irritation may cause the food pipe to become inflamed. Sores called ulcers may form.
Symptoms may include:
- Cough
- Difficulty swallowing
- Painful swallowing
- Heartburn (acid reflux)
- Hoarseness
- Sore throat
Exams and Tests
The doctor may perform the following tests:
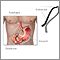
- Esophageal manometry
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), removing a piece of tissue from the food pipe for examination (biopsy)
- Upper GI series (barium swallow x-ray)
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause. Common treatment options are:
- Medicines that reduce stomach acid in case of reflux disease
- Antibiotics to treat infections
- Medicines and diet changes to treat eosinophilic esophagitis
- Medicines to coat the lining of the food pipe to treat damage related to pills
You should stop taking medicines that damage the lining of the esophagus. Take your pills with plenty of water. Avoid lying down immediately after taking the pill.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, the disorders that cause swelling and inflammation of the food pipe, respond to treatment.
Possible Complications
If not treated, this condition may cause severe discomfort. Scarring (stricture) of the food pipe may develop. This can cause swallowing problems.
A condition called Barrett esophagus (BE) can develop after years of GERD. Rarely, BE may lead to cancer of the food pipe.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have:
- Frequent symptoms of esophagitis
- Difficulty swallowing
References
Falk GW, Katzka DA. Diseases of the esophagus. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 129.
Graman PS. Esophagitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 97.
Richter JE, Vaezi MF. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 46.
Review Date: 7/30/2022
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.