Cataract - adult
Lens opacity; Age-related cataract; Vision loss - cataract
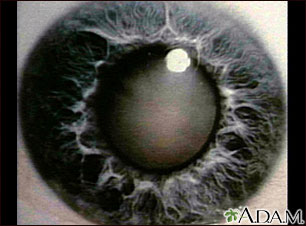
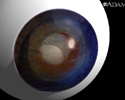
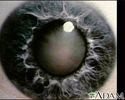
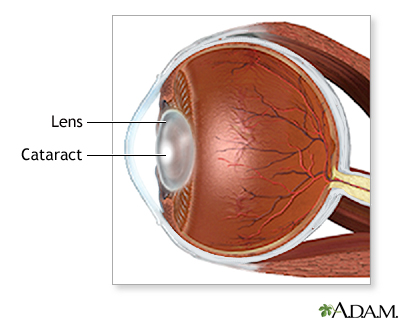
A cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye.
Causes
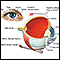
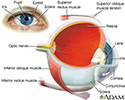
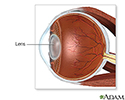
The lens of the eye is normally clear. It acts like the lens on a camera, focusing light as it passes to the back of the eye.
Until a person is around age 45, the shape of the lens is able to change. This allows the lens to focus on an object, whether it is close or far away.
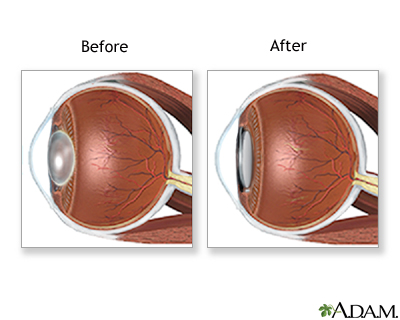
As a person ages, proteins in the lens begin to break down. This makes the lens less flexible so that it is harder to focus on near objects. Over time, the lens becomes cloudy. What the eye sees may appear blurry at all distances. This condition is known as a cataract.
Factors that may speed cataract formation are:
- Diabetes
- Eye inflammation
- Eye injury
- Family history of cataracts
- Long-term use of corticosteroids (taken by mouth) or certain other medicines
- Radiation exposure
- Smoking
- Surgery for another eye problem
- Too much exposure to ultraviolet light (sunlight)
Symptoms
Cataracts develop slowly and painlessly. Vision in the affected eye slowly gets worse.
- Mild clouding of the lens often occurs after age 60. But it may not cause any vision problems.
- By age 75, most people have cataracts that affect their vision.
Problems with seeing may include:
- Being sensitive to glare
- Cloudy, fuzzy, foggy, or filmy vision
- Difficulty seeing at night or in dim light
- Double vision
- Loss of color intensity
- Problems seeing shapes against a background or the difference between shades of colors
- Seeing halos around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass prescriptions
Cataracts lead to decreased vision, even in daylight. Most people with cataracts have similar changes in both eyes, though one eye may be worse than the other. Often there are only mild vision changes.
Exams and Tests
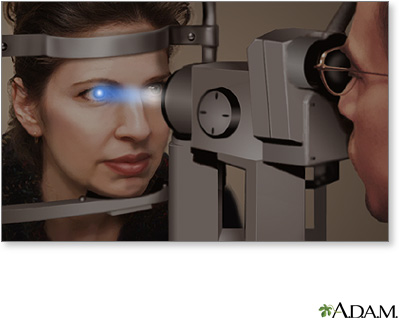
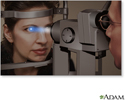
A standard eye exam and slit-lamp examination are used to diagnose cataracts. Other tests are rarely needed, except to rule out other causes of poor vision.
Treatment
For early cataract, the eye doctor (ophthalmologist) may recommend the following:
- Change in eyeglass prescription
- Better lighting
- Magnifying lenses
- Sunglasses
As vision gets worse, you may need to make changes around the home to avoid falls and injuries.
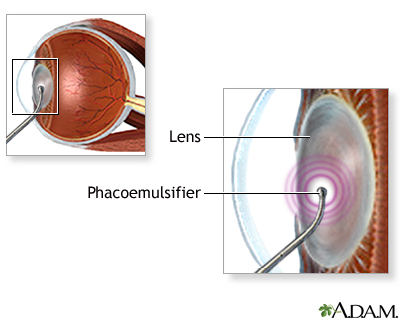
The only treatment for a cataract is surgery to remove it. If a cataract is not making it hard for you to see, surgery is usually not needed. Cataracts usually do not harm the eye, so you can have surgery when you and your eye doctor decide it is right for you. Surgery is usually recommended when you can't do normal activities such as driving, reading, or looking at computer or video screens, even with glasses.
Some people may have other eye problems, such as diabetic retinopathy, that can't be treated without first having cataract surgery.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Vision may not improve to 20/20 after cataract surgery if other eye diseases, such as macular degeneration, are present. The eye doctor can often determine this in advance.
Possible Complications
Early diagnosis and properly timed treatment are key to preventing permanent vision problems.
Although rare, a cataract that goes on to an advanced stage (called a hypermature cataract) can begin to leak into other parts of the eye. This may cause a painful form of glaucoma and inflammation inside the eye.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your eye care professional for an appointment if you have:
- Decreased night vision
- Problems with glare
- Vision loss
Prevention
The best prevention involves controlling diseases that increase the risk for a cataract. Avoiding exposure to things that promote cataract formation can also help. For example, if you smoke, now is the time to quit. Also, when outdoors, wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from harmful UV rays.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Preferred Practice Patterns Cataract and Anterior Segment Panel, Hoskins Center for Quality Eye Care. Cataract in the adult eye PPP - 2021. www.aao.org/preferred-practice-pattern/cataract-in-adult-eye-ppp-2021-in-press. Updated November 2021. Accessed December 1, 2021.
Cataract /Anterior Segment Summary Benchmark – 2020, AAO PPP Cataract and Anterior Segment Panel, Hoskins Center for Quality Eye Care.www.aao.org/summary-benchmark-detail/cataract-anterior-segment-summary-benchmark-2020. Updated December 2021. Accessed January 20, 2022.
Wevill M. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, causes, morphology, and visual effects of cataract. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 5.3.
Cataract
Animation
Cataracts
Animation
Eye - illustration
Eye
illustration
Slit-lamp exam - illustration
Slit-lamp exam
illustration
Cataract - close-up of the eye - illustration
Cataract - close-up of the eye
illustration
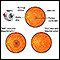
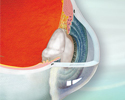
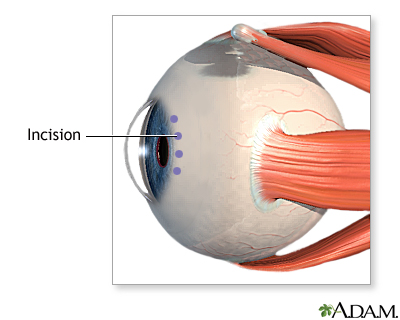
Cataract surgery - series - Normal anatomy
Presentation
Review Date: 9/3/2021
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 02/15/2023.