Health Library
Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
Air around the lung; Air outside the lung; Pneumothorax dropped lung; Spontaneous pneumothorax
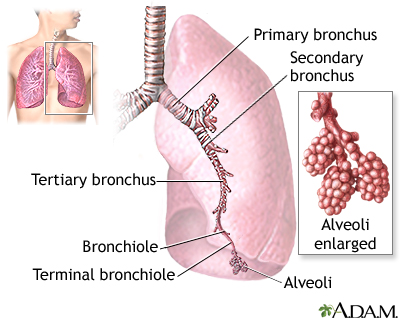
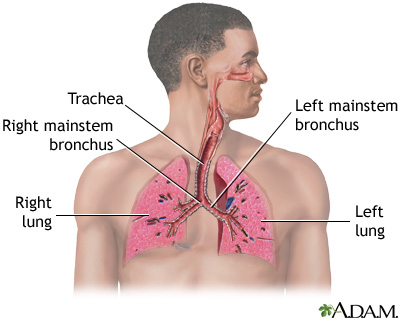
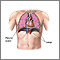
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This buildup of air puts pressure on the lung, so it cannot expand as much as it normally does when you take a breath.
The medical name of this condition is pneumothorax.
Images
Presentation
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Collapsed lung can be caused by an injury to the lung. Injuries can include a gunshot or knife wound to the chest, rib fracture, or certain medical procedures.
In some cases, a collapsed lung is caused by air blisters (blebs) that break open, sending air into the space around the lung. This can result from air pressure changes such as when scuba diving or traveling to a high altitude.
Tall, thin people and smokers are more at risk for a collapsed lung.
Lung diseases can also increase the chance of getting a collapsed lung. These include:
In some cases, a collapsed lung occurs without any cause. This is called a spontaneous collapsed lung.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of a collapsed lung include:
- Sharp chest or shoulder pain, made worse by a deep breath or a cough
- Shortness of breath
- Nasal flaring (from shortness of breath)
A larger pneumothorax causes more severe symptoms, including:
- Bluish color of the skin due to lack of oxygen
- Chest tightness
- Lightheadedness and near fainting
- Easy fatigue
- Abnormal breathing patterns or increased effort of breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Shock and collapse
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will listen to your breathing with a stethoscope. If you have a collapsed lung, there are decreased breath sounds or no breath sounds on the affected side. You may also have low blood pressure.
Tests that may be ordered include:
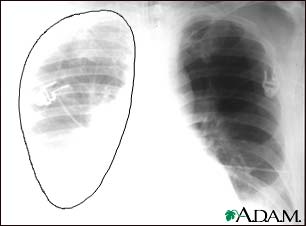
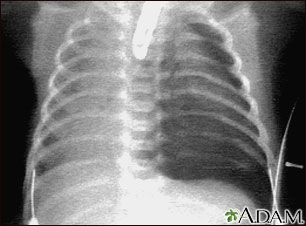
- Chest x-ray
- Arterial blood gases and other blood tests
- CT scan if other injuries or conditions are suspected
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Treatment
A small pneumothorax may go away on its own over time. You may only need oxygen treatment and rest.
The provider may use a needle to allow the air to escape from around the lung so it can expand more fully. You may be allowed to go home if you live near the hospital.
If you have a large pneumothorax, a chest tube will be placed between the ribs into the space around the lungs to help drain the air and allow the lung to re-expand. The chest tube may be left in place for several days and you may need to stay in the hospital. If a small chest tube or flutter valve is used, you may be able to go home. You will need to return to the hospital to have the tube or valve removed.
Some people with a collapsed lung need extra oxygen.
Lung surgery may be needed to treat collapsed lung or to prevent future episodes. The area where the leak occurred may be repaired. Sometimes, a special chemical is placed into the area of the collapsed lung. This chemical causes a scar to form. This procedure is called pleurodesis.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If you have a collapsed lung, you are more likely to have another one in the future if you:
- Are tall and thin
- Continue to smoke
- Have had two collapsed lung episodes in the past
How well you do after having a collapsed lung depends on what caused it.
Possible Complications
Complications may include any of the following:
- Another collapsed lung in the future
- Shock, if there are serious injuries or infection, severe inflammation, or fluid in the lung develops
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have symptoms of a collapsed lung, especially if you have had one before.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent a collapsed lung. Following standard procedure can reduce the risk of a pneumothorax when scuba diving. You can decrease your risk by not smoking.
Related Information
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)Asthma
Cystic fibrosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Pertussis
References
Byyny RL, Shockley LW. Scuba diving and dysbarism. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 135.
Hallifax R, Rahman NM. Pneumothorax. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 110.
Raja AS. Thoracic trauma. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 38.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/12/2021
Reviewed By: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2021 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
