Vesicles
Blisters
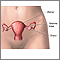
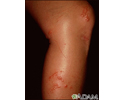
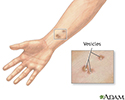
A vesicle is a small fluid-filled blister on the skin.
Considerations
A vesicle is small. It may be as tiny as the top of a pin or up to 5 millimeters wide. A larger blister is called a bulla.
In many cases, vesicles break easily and release their fluid onto the skin. When this fluid dries, yellow crusts may remain on the skin surface.
Causes
Many diseases and conditions can cause vesicles. Common examples include:
- Allergic reactions to drugs
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
- Autoimmune disorders such as bullous pemphigoid or pemphigus
- Blistering skin diseases including porphyria cutanea tarda and dermatitis herpetiformis
- Chickenpox
- Contact dermatitis (may be caused by poison ivy)
- Herpes simplex (cold sores, genital herpes)
- Herpes zoster (shingles)
- Bacterial infections
- Fungal infections
- Burns
- Friction
- Treatment with cryotherapy (to treat a wart for example)
Home Care
It is best to have your health care provider examine any skin rashes, including vesicles.
Over-the-counter treatments are available for certain conditions that cause vesicles, including poison ivy and cold sores.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have any unexplained blisters on your skin.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will look at your skin. Some vesicles can be diagnosed simply by how they look.
In many cases, additional tests are needed. The fluid inside a blister may be sent to a lab for closer examination. In particularly difficult cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to make or confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment will depend on the cause of the vesicles.
References
Dinulos JGH. Vesicular and bullous diseases. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Marks JG, Miller JJ. Vesicles and bullae. In: Marks JG, Miller JJ, eds. Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 10.
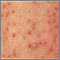
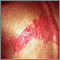
Bullous pemphigoid - close-up of tense blisters - illustration
Bullous pemphigoid - close-up of tense blisters
illustration
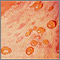
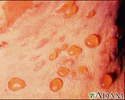
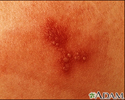
Chigger bite - close-up of blisters - illustration
Chigger bite - close-up of blisters
illustration
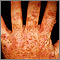
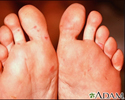
Hand, foot, and mouth disease on the soles - illustration
Hand, foot, and mouth disease on the soles
illustration
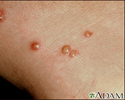
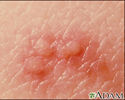
Herpes simplex - close-up - illustration
Herpes simplex - close-up
illustration
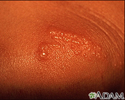
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion - illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion
illustration
Poison ivy on the knee - illustration
Poison ivy on the knee
illustration
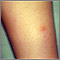
Poison ivy on the leg - illustration
Poison ivy on the leg
illustration
Vesicles - illustration
Vesicles
illustration
Bullous pemphigoid - close-up of tense blisters - illustration
Bullous pemphigoid - close-up of tense blisters
illustration
Chigger bite - close-up of blisters - illustration
Chigger bite - close-up of blisters
illustration
Hand, foot, and mouth disease on the soles - illustration
Hand, foot, and mouth disease on the soles
illustration
Herpes simplex - close-up - illustration
Herpes simplex - close-up
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion - illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion
illustration
Poison ivy on the knee - illustration
Poison ivy on the knee
illustration
Poison ivy on the leg - illustration
Poison ivy on the leg
illustration
Vesicles - illustration
Vesicles
illustration
Review Date: 6/19/2021
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.