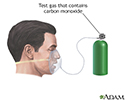
Lung diffusion testing
Diffusing capacity; DLCO test
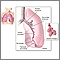
Lung diffusion testing measures how well the lungs exchange gases. This is an important part of lung testing, because the major function of the lungs is to allow oxygen to "diffuse" or pass into the blood from the lungs, and to allow carbon dioxide to "diffuse" from the blood into the lungs.
How the Test is Performed
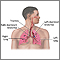
You breathe in (inhale) air containing a very small amount of carbon monoxide and a tracer gas, such as methane or helium. You hold your breath for 10 seconds, then rapidly blow it out (exhale). The exhaled gas is tested to determine how much of the tracer gas was absorbed during the breath.
How to Prepare for the Test
Before taking this test:
- Do not eat a heavy meal before the test.
- Do not smoke for at least 4 to 6 hours before the test.
- If you use a bronchodilator or other inhaled medicines, ask your health care provider whether or not you can use them before the test.
How the Test will Feel
The mouthpiece fits tightly around your mouth. Clips are put on your nose.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is used to diagnose certain lung diseases, and to monitor the status of people with established lung disease. Repeatedly measuring the diffusing capacity can help determine whether the disease is improving or getting worse.
Normal Results
Normal test results depend on a person's:
- Age
- Sex
- Height
- Hemoglobin (the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen) level
What Abnormal Results Mean
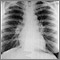
Abnormal results mean that gases do not move normally across the lung tissues into the blood vessels of the lung. This may be due to lung diseases such as:
- COPD
- Interstitial fibrosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Sarcoidosis
- Bleeding in the lung
- Asthma
- Reduced lung volumes (capacity)
Risks
There are no significant risks.
Considerations
Other pulmonary function tests may be done together with this test.
References
Bhakta NR, Kaminsky DA. Pulmonary function testing: Physiologic and technical principles. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 31.
Scanlon PD. Respiratory function: mechanisms and testing. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 79.
Review Date: 12/6/2021
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.