Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
COPD; Chronic obstructive airways disease; Chronic obstructive lung disease; Chronic bronchitis; Emphysema; Bronchitis - chronic
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe.
There are two main forms of COPD:
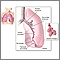
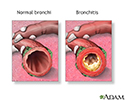
- Chronic bronchitis, which involves a long-term cough with mucus
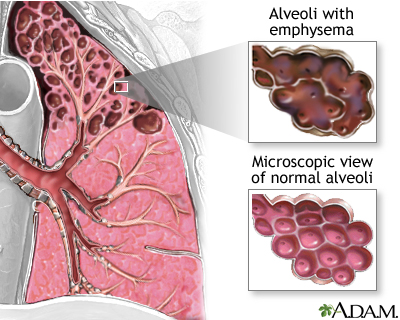
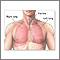
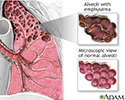
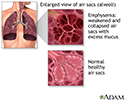
- Emphysema, which involves damage to the lungs over time
Most people with COPD have a combination of both conditions.
Causes
Smoking is the main cause of COPD. The more a person smokes, the more likely that person will develop COPD. But some people smoke for years and never get COPD.
If a person has a rare condition in which they lack a protein called alpha-1 antitrypsin, they can develop emphysema even without smoking.
Other risk factors for COPD are:
- Exposure to certain gases or fumes in the workplace
- Exposure to heavy amounts of secondhand smoke and pollution
- Frequent use of a cooking fire without proper ventilation
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Cough, with or without mucus
- Fatigue
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea) that gets worse with mild activity
- Trouble catching one's breath
- Wheezing
Because the symptoms develop slowly, many people may not know that they have COPD.
Exams and Tests
The best test for COPD is a lung function test called spirometry. This involves blowing out as hard as possible into a small machine that tests lung capacity. The results can be checked right away.
Using a stethoscope to listen to the lungs can also be helpful, showing prolonged expiratory time or wheezing. But sometimes, the lungs sound normal, even when a person has COPD.
Imaging tests of the lungs, such as x-rays and CT scans may be ordered. With an x-ray, the lungs may look normal, even when a person has COPD. A CT scan will almost always show signs of COPD if it is present.
Sometimes, a blood test called arterial blood gas may be done to measure the amounts of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
If your health care provider suspects you have alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, a blood test will likely be ordered to detect this condition.
Treatment
There is no cure for COPD. But there are many things you can do to relieve symptoms and keep the disease from getting worse.
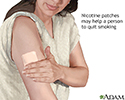
If you smoke, now is the time to quit. This is the best way to slow lung damage.
Medicines used to treat COPD include:
- Quick-relief drugs to help open the airways
- Control drugs to reduce lung inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling in the airways
- Certain long-term antibiotics
In severe cases or during flare-ups, you may need to receive:
- Steroids by mouth or through a vein (intravenously)
- Bronchodilators through a nebulizer
- Oxygen therapy
- Assistance from a machine to help breathing by using a mask or through the use of an endotracheal tube
Your provider may prescribe antibiotics during symptom flare-ups, because an infection can make COPD worse.
You may need oxygen therapy at home if you have a low level of oxygen in your blood.
Pulmonary rehabilitation does not cure COPD. But it can teach you more about the disease, train you to breathe in a different way so you can stay active and feel better, and keep you functioning at the highest level possible.
You can do things every day to keep COPD from getting worse, protect your lungs, and stay healthy.
Walk to build up strength:
- Ask the provider or therapist how far to walk.
- Slowly increase how far you walk.
- Avoid talking if you get short of breath when you walk.
- Use pursed lip breathing when you breathe out, to empty your lungs before the next breath.
Things you can do to make it easier for yourself around the home include:
- Avoid very cold air or very hot weather
- Make sure no one smokes in your home
- Reduce air pollution by not using the fireplace and getting rid of other irritants
- Manage stress and your mood
- Use oxygen if prescribed for you
Eat healthy foods, including fish, poultry, and lean meat, as well as fruits and vegetables. If it is hard to keep your weight up, talk to a provider or dietitian about eating foods with more calories.
Surgery or other interventions may be used to treat COPD. Only a few people benefit from these surgical treatments:
- One-way valves can be inserted with a bronchoscopy to help deflate parts of the lung that are hyperinflated (overinflated) in select patients.
- Surgery to remove parts of the diseased lung, which can help less-diseased parts work better in some people with emphysema (lung volume reduction surgery).
- Lung transplant for a small number of very severe cases.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Outlook (Prognosis)
COPD is a long-term (chronic) illness. The disease will get worse more quickly if you do not stop smoking.
If you have severe COPD, you will be short of breath with most activities. You may be admitted to the hospital more often.
Talk with your provider about breathing machines and end-of-life care as the disease progresses.
Possible Complications
With COPD, you may have other health problems such as:
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Need for breathing machine support with a mask (non-invasive ventilation) and oxygen therapy
- Right-sided heart failure or cor pulmonale (heart swelling and heart failure due to chronic lung disease)
- Pneumonia
- Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
- Severe weight loss and malnutrition
- Thinning of the bones (osteoporosis)
- Debilitation
- Increased anxiety
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have a rapid increase in shortness of breath.
Prevention
Not smoking prevents most COPD. Ask your provider about quit-smoking programs. Medicines are also available to help you stop smoking.
References
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) website. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: 2023 Report. goldcopd.org/2023-gold-report-2/. Accessed January 6, 2023.
Han MK, Lazarus SC. COPD: diagnosis and management. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 64.
National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute website. COPD national action plan. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/COPD%20National%20Action%20Plan%20508_0.pdf. Updated February 2021. Accessed July 13, 2022.
Rochester CL, Nici L. Pulmonary rehabilitation. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 139.
Smoking tips to quit
Animation
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Animation
Spirometry - illustration
Spirometry
illustration
Emphysema - illustration
Emphysema
illustration
Bronchitis - illustration
Bronchitis
illustration
Quitting smoking - illustration
Quitting smoking
illustration
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder) - illustration
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder)
illustration
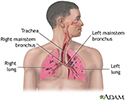
Respiratory system - illustration
Respiratory system
illustration
Spirometry - illustration
Spirometry
illustration
Emphysema - illustration
Emphysema
illustration
Bronchitis - illustration
Bronchitis
illustration
Quitting smoking - illustration
Quitting smoking
illustration
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder) - illustration
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder)
illustration
Respiratory system - illustration
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 4/2/2022
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 01/06/2023.