Lactic acid test
Lactate test
Lactic acid is mainly produced in muscle cells and red blood cells. It forms when the body breaks down carbohydrates to use for energy when oxygen levels are low. Times when your body's oxygen level might drop include:
- During intense exercise
- When you have an infection or disease that reduces oxygen delivery to your body tissues
A test can be done to measure the amount of lactic acid in the blood.
How the Test is Performed
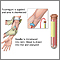
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
How to Prepare for the Test
DO NOT exercise for several hours before the test. Exercise can cause a temporary increase in lactic acid levels.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted. You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is most often done to diagnose lactic acidosis.
Normal Results
Normal results range from 4.5 to 19.8 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) (0.5 to 2.2 millimoles per liter [mmol/L]).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results mean that body tissues are not getting enough oxygen.
Conditions that can increase lactic acid levels include:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Heart failure
- Liver disease
- Lung disease
- Medicines such as beta adrenergic agonists (albuterol, salmeterol), certain HIV medicines, metformin
- Not enough blood containing oxygen getting to a certain area of the body
- Severe infection that affects the entire body (sepsis)
- Very low levels of oxygen in the blood (hypoxia)
Considerations
Clenching the fist or having the elastic band in place for a long time while having blood drawn can result in a false increase in lactic acid level.
References
Neligan PJ. How should acid-base disorders be diagnosed? In: Deutschman CS, Neligan PJ, eds. Evidence-Based Practice of Critical Care. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 59.
Seifter JL. Acid-base disorders. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 110.
Tallentire VR, MacMahon MJ. Acute medicine and critical illness. In: Ralston SH, Penman ID, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 10.
Review Date: 5/1/2021
Reviewed By: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.