Pectus excavatum
Funnel chest; Cobbler's chest; Sunken chest
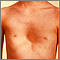
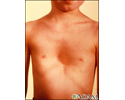
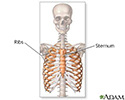
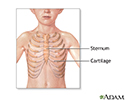
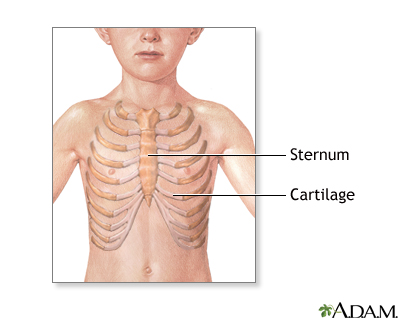
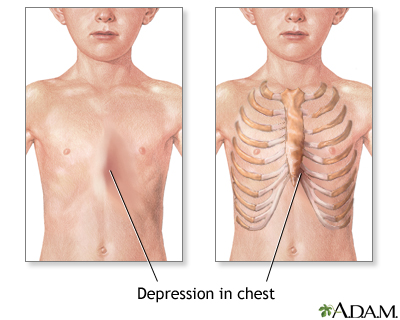
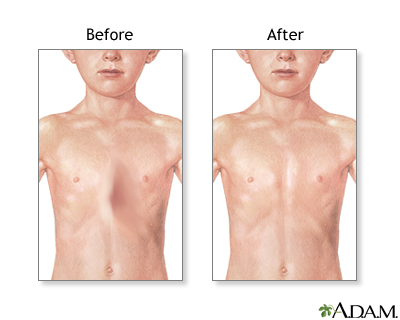
Pectus excavatum is a medical term that describes an abnormal formation of the rib cage that gives the chest a caved-in or sunken appearance.
Considerations
Pectus excavatum occurs in a baby who is developing in the womb. It can also develop in a baby after birth. The condition can be mild or severe.
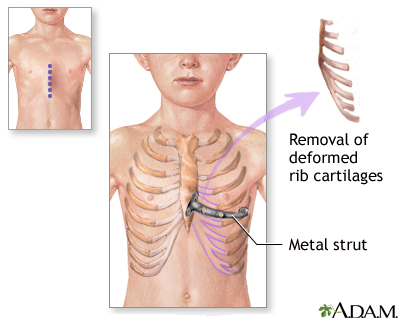
Pectus excavatum is due to too much growth of the connective tissue that joins the ribs to the breastbone (sternum). This causes the sternum to grow inward. As a result, there is a depression in the chest over the sternum, which may appear quite deep.
If the condition is severe, the heart and lungs can be affected. Also, the way the chest looks may cause emotional stress for the child.
Causes
The exact cause is unknown. Pectus excavatum occurs by itself. Or there may be a family history of the condition. Other medical problems linked with this condition include:
- Marfan syndrome (connective tissue disease)
- Noonan syndrome (disorder that causes many parts of the body to develop abnormally)
- Poland syndrome (disorder that causes muscles to not develop fully or at all)
- Rickets (softening and weakening of the bones)
- Scoliosis (abnormal curving of the spine)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you or your child has any of the following:
- Chest pain
- Trouble breathing
- Feelings of depression or anger about the condition
- Feeling tired, even when not being active
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical examination. An infant with pectus excavatum may have other symptoms and signs that, when taken together, define a specific condition known as a syndrome.
The provider will also ask about medical history, such as:
- When was the problem first noticed?
- Is it getting better, worse, or staying the same?
- Do other family members have an unusual-shaped chest?
- What other symptoms are there?
Tests may be done to rule out suspected disorders. These tests may include:
- Chromosome studies
- Enzyme assays
- Metabolic studies
- X-rays
- CT scan
Tests may also be done to find out how severely the lungs and heart are affected.
This condition can be surgically repaired. Surgery is generally advised if there are other health problems, such as trouble breathing. Surgery may also be done to improve the appearance of the chest. Talk to your provider about treatment options.
References
Boas SR. Skeletal diseases influencing pulmonary function. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 445.
Danielson PD, Colombani PM. Repair of pectus excavatum. In: Cameron AM, Cameron JL, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2020:897-900.
Gottlieb LJ, Reid RR, Slidell MB. Pediatric chest and trunk defects. In: Rodriguez ED, Losee JE, Neligan PC, eds. Plastic Surgery: Volume 3: Craniofacial, Head and Neck Surgery and Pediatric Plastic Surgery. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 40.
Review Date: 7/15/2021
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.